|
ITACONIC ACID |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. |
97-65-4 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 202-599-6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
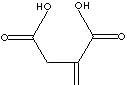
| FORMULA | HOOCCH2C(=CH2)COOH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. |
131.10 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
H.S. CODE |
2917.19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | Methylenesuccinic acid; Methylene Butanedioic acid; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Propylenedicarboxylic acid; 2-Propene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid; | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
white crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
MELTING POINT |
165 - 169 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.5 - 1.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
8 - 9.5 % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
Soluble in alcohol. slightly soluble in organic solvents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NFPA RATINGS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Hygroscopic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Itaconic Acid (also called Methylene Succinic Acid) is a white crystalline
carboxylic acid obtained by the fermentation of carbohydrates. It is soluble in
water, ethanol and acetone. Unsaturated solid bond makes a conjugated system
with carbonly group. It is used in the field of;
The end applications of itaconic acid and its esters include in the field of co-polymerizations, plasticizers, lubricant oil, paper coating. carpets for better duration, adhesives, coatings, paints, thickener, emulsifier, surface active agents, pharmaceuticals and printing chemicals. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PURITY |
99.5% min | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
MELTING POINT |
165 - 169 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
0.3% max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
0.03% max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
IRON (as Fe) |
10ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CHLORIDE (as CI) |
10ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SULPHATE (as SO4) |
50ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
HEAVY METALS (as Pb) |
10ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 25kgs in bag | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 33/36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 24/25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF DICARBOXYLIC ACID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dicarboxylic
acid is a compound containing two carboxylic acid, -COOH,
groups. Examples are shown in table. In substitutive
nomenclature their names are formed by adding -dioic'
as a suffix to the name of the parent compound. They
can yield two kinds of salts, as they contain two carboxyl
groups in its molecules.
There are almost infinite esters obtained from thousands of potential starting materials. Esters are formed by removal of water from an acid and an alcohol, e.g., carboxylic acid esters, phosphoric acid esters, and sulfonic acid esters. Carboxylic acid esters are used as in a variety of direct and indirect applications. Lower chain esters are used as flavouring base materials, plasticizers, solvent carriers and coupling agents. Higher chain compounds are used as components in metalworking fluids, surfactants, lubricants, detergents, oiling agents, emulsifiers, wetting agents textile treatments and emollients, They are also used as intermediates for the manufacture of a variety of target compounds. The almost infinite esters provide a wide range of viscosity, specific gravity, vapor pressure, boiling point, and other physical and chemical properties for the proper application selections. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||